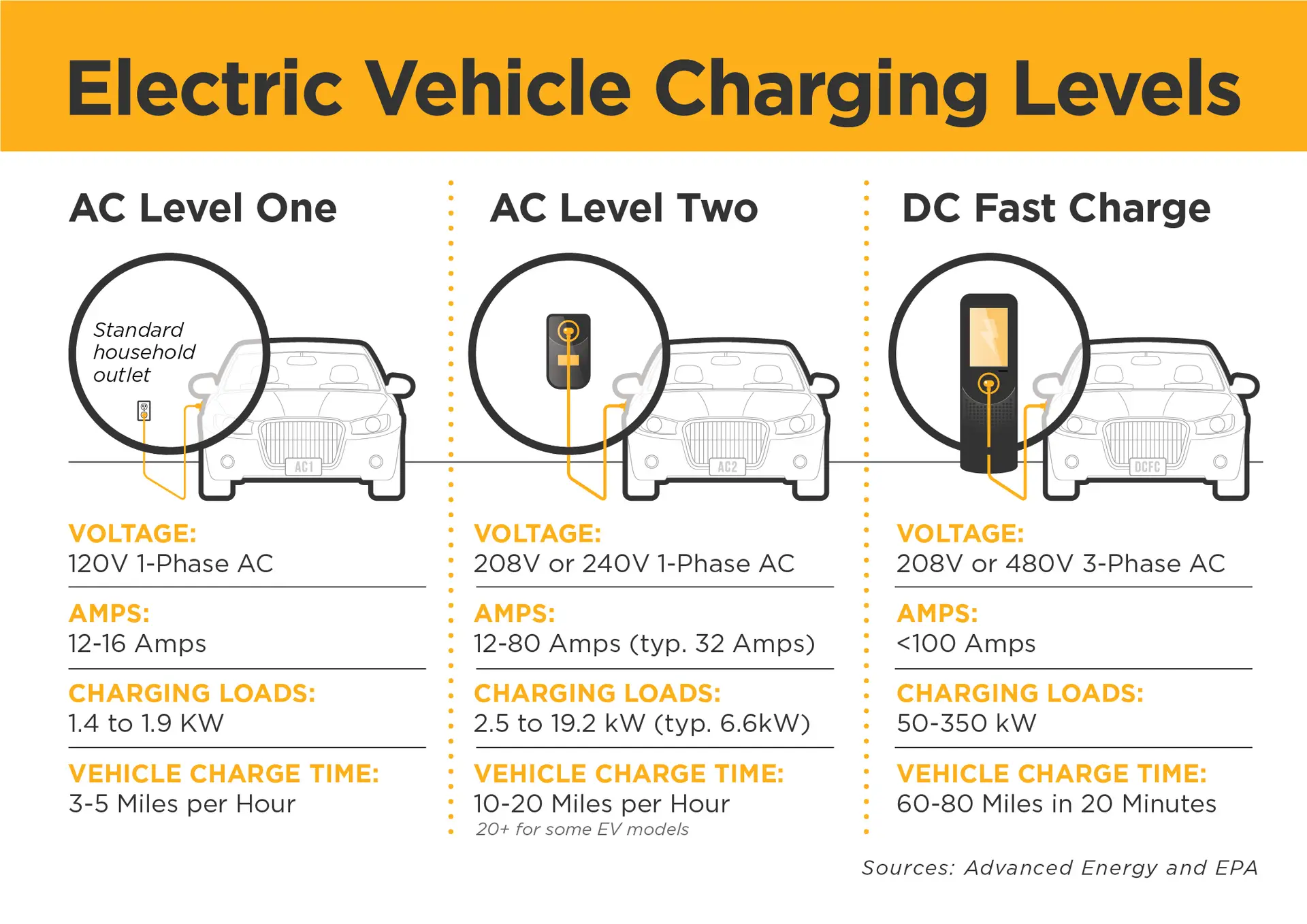
Electric vehicle (EV) owners have multiple options for charging their vehicles. There are three common EV charging levels: Level One, Level Two and DC Fast Charge.
Level One Charging
Level One charging is the simplest and slowest way to charge your EV. It uses a standard 120-volt outlet that you can find in most homes. You can plug your EV into any outlet with the equipment that comes with your car. Level One charging does not require any additional installation or cost, but it will take a long time to charge your EV. You can expect to add 3-5 miles of range per hour of charging with Level One. The average American commute is less than 40 miles round trip, so this level of charging can be adequate for drivers who have plenty of time to charge overnight.
Level Two Charging
Level Two charging is faster and more convenient than Level One, but it requires some investment and installation. It uses a 240-volt circuit that is similar to the ones used for large appliances like dryers or stoves. You will need to buy a separate Level Two charger and have it installed by a licensed electrician in your garage or carport. Level Two charging can add 10-20 miles of range per hour of charging, depending on your car and charger. This level of charging is ideal for daily drivers who want to charge their EVs quickly and reliably.
Level One and Two chargers are also known as destination chargers, because they are usually used where the EV is parked for a long time, such as at home or work. These chargers deliver AC electricity to the car, where it is converted to DC by the onboard charger. The term charger is actually a misnomer here, because the real charger is inside the car. A more technical term is Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment or EVSE, but most people colloquially call them chargers. Destination charging is the most affordable and efficient way to keep your EV charged.
DC Fast Charging
DC Fast Charge stations are different from Level One and Two chargers, because they deliver DC electricity directly to the car’s battery, bypassing the onboard charger. This allows them to charge the EV much faster than AC chargers, but also more expensively. DC Fast Charge stations are usually located near highways or busy public areas, where drivers need a quick boost of range. They can add 60-80+ miles of range in just 20 minutes, depending on the car and station. However, DC Fast Charge stations are not compatible with all EVs, and they may degrade the battery life if used too often. This level of charging is best for occasional long-distance trips or for drivers without access to destination charging.